- Item
- 1955-07-05
Part of Richards Studio Photographs
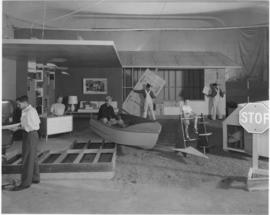
Advertising set up for plywood, the building material of 1,000 uses. Photograph ordered by the Condon Co. for an ad in Life magazine for the Douglas Fir Plywood Association. The year of 1955 marked the fiftieth anniversary of the invention of plywood panels. The DFPA used this opportunity to further promote their product. Plywood is shown being used left to right as woodworking materials, in flooring, as furniture, in boats, as house siding, playground building materials, a doghouse for a real pig and in traffic signs. This surrealistic overview would be sure to catch the readers eye in the magazine.
Plywood; Douglas Fir Plywood Association (Tacoma)--Products;